Understanding the bones structure of the skull is fondamental when performing facial treatments :
Bones of the Cranium :
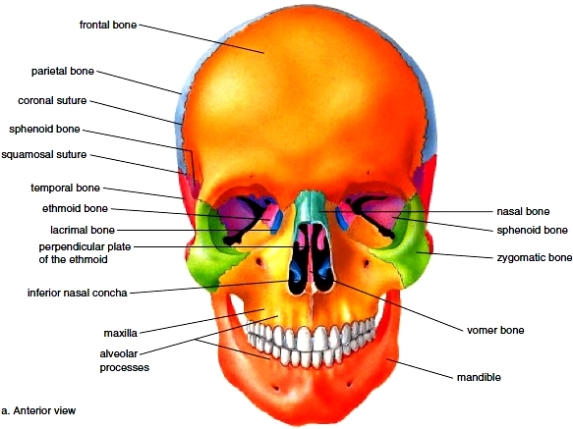
- 1 Frontal Bone
- 2 x Parietal bones
- 2 x temporal bones
- 1 x occipital bone
- 1 x sphenoid bone (butterfly shape in the base of the skull)
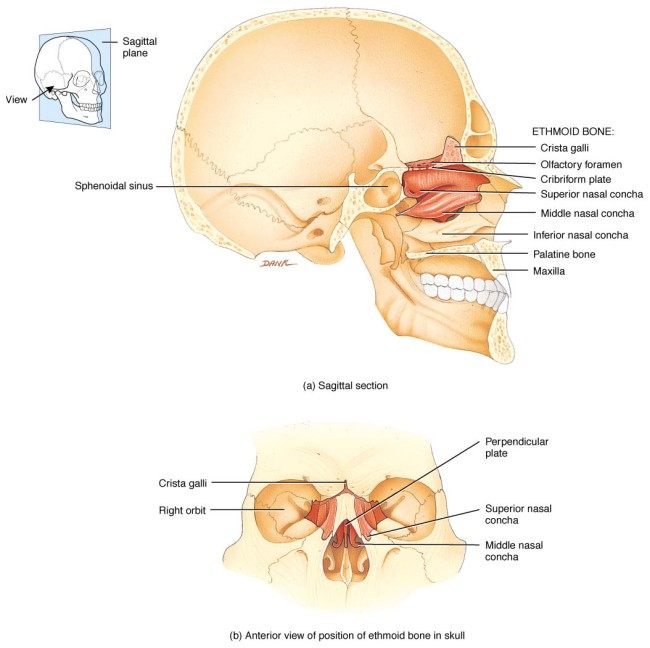
- 1x ethmoid bone
Bones of the face :
- 2x maxillae bones
- 1 x mandible bone
- 2 x zygomatic bones
- 2 x nasal bones
Internal Facial bones
- 2 x pallatine bones
- 1 x vomer bone
- 2 x lacrimal bones
- 2 x turbinate bones (inferior conchae)
Bones of the eye orbit :
- Frontal
- Ethmoid
- Lacrimal
- Sphenoid
- Temporal
- Maxillae
- Palatine
- Zygomatic
The Cranium:
- 1 frontal bone : The frontal bone is a large bone which forms the forehead and upper part of the eye socket. It is joined to the two Parietal by a serrated articulation. (SUTURE)
- 2x Parietal bones: One on either side of the dome of the skull. These two bones are the largest part of the cranium.
- 1x occipital bone situated at the back and the base of the skull. It has a large opening through which the spinal cord passes and it articulates with the vertebral column.
- 1x sphenoid bone this is a bat (butterfly ) shape bone the wings extend outwards to the side of the cranium articulating with the temporal,parietal and frontal bone. The optic nerve and opthalmic artery pass through a round opening.
- 1x ethmoid bone this lies in front of the sphenoid bone and below the frontal bone to form part of the nasal cavities and part of the eye orbits. It is a very delicate bone containing many air sinus.
SINUSES : These contain air and are lined with ciliated mucous membrane. They give resonance to the voice and lighten the bones of the face and cranium,making it easier for teh skull to balance on the vertebral column.
SUTURE: a joint containing fibrous tissue between the bones. Sutures become less evident with age and the bones become fused.